Welcome to our guide on understanding torrents! In this article, we will explore the world of torrenting and how it revolutionizes the distribution and downloading of large files. Torrents operate on a peer-to-peer (P2P) network architecture, allowing users to directly share and receive files from one another. This method is especially efficient for downloading large files as it breaks them into smaller pieces and enables simultaneous downloading from multiple sources.
Through the use of the BitTorrent protocol, torrents provide an effective means of file sharing. But how do they work? We'll delve into the intricacies of torrenting, including the role of torrent clients, metadata, seeders, leechers, and swarms. We'll also explore the function of torrent indexers and trackers, as well as the convenience of magnet links. Additionally, we'll cover the benefits of utilizing torrents, legal and ethical concerns, and how to stay safe while torrenting.
As we conclude our discussion, we'll take a glimpse into the future of torrenting and how evolving technologies and the legal landscape may shape this method of file sharing moving forward. Whether you are new to torrenting or seeking a deeper understanding, join us on this journey to demystify the world of torrents!
Key Takeaways:
- Torrents operate on a peer-to-peer (P2P) network architecture, enabling efficient file distribution and downloading of large files.
- The BitTorrent protocol breaks files into smaller pieces, facilitating faster downloads and more efficient transfers.
- Torrent clients interpret torrent files and connect users to the P2P network.
- Seeders are users who share complete files, while leechers are downloading users.
- Torrent indexers host torrent files, and trackers facilitate the exchange of data between users.
How Torrents Work
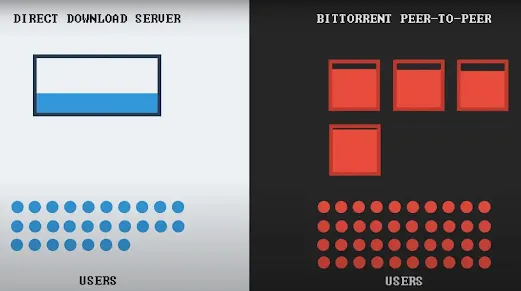
Torrents operate on a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, where users connect with others who possess the same file. This decentralized approach allows for faster downloads and reduces the strain on individual servers. The BitTorrent protocol, introduced by Bram Cohen in 2001, revolutionized file distribution by breaking files into smaller pieces for simultaneous downloading and sharing.
Under the BitTorrent protocol, files are divided into small chunks, known as "pieces," which can be downloaded and shared simultaneously by multiple users. This approach significantly improves download speed and ensures more efficient file transfers.
When a user downloads a torrent file, their torrent client connects to other peers in the network and begins to exchange pieces of the file. Each user acts as both a downloader and an uploader, maximizing the availability and speed of the file. As users complete their downloads, they become additional sources, known as "seeders," making the file available to others.
This peer-to-peer networking model eliminates the need for a central server to facilitate file transfers. Instead, users directly connect and share files, making the process more efficient and reliable. The distributed nature of torrents ensures that files are readily available even if individual users go offline, providing a robust and resilient network for file sharing.
"By leveraging P2P networking through the BitTorrent protocol, torrents enable users to download and share files simultaneously, resulting in significant speed improvements and efficient distribution."
Benefits of Torrents
The use of the BitTorrent protocol and P2P networking offers several advantages:
- Efficient Distribution: Torrents divide files into smaller pieces, allowing for faster overall download speeds.
- Bandwidth-Efficient: Users share the load of distributing the file, reducing strain on individual servers and ensuring a more balanced distribution of bandwidth.
- Robust and Resilient: The decentralized nature of torrents means files remain available even if individual users go offline.
The Future of Torrenting
As technology continues to evolve, torrenting is likely to adapt and incorporate new advancements. Emerging technologies may enhance the efficiency and security of torrenting, providing users with even better experiences. However, the legal landscape around torrents varies by jurisdiction, and it is essential for torrenting communities to navigate these challenges while respecting the rights of content creators.
Torrent Clients and Metadata
Torrent clients are essential software applications for efficiently downloading and sharing torrent files. These clients interpret the torrent files, which contain valuable metadata about the files being shared and information about the network.
When you obtain a torrent file, you gain access to the metadata that describes the contents of the file, such as the file name, size, and file structure. Additionally, the metadata includes crucial information about the network, such as the addresses of other peers or computers that are also sharing the file.
Obtaining torrent files is typically done through torrent indexing websites or torrent search engines that provide a repository of available files. These sites act as a directory where users can search and find the desired torrents based on their interests and requirements.
The torrent files you obtain from these sources serve as a blueprint for the torrent client to connect to the network and initiate the downloading process.
Once you load a torrent file into your chosen torrent client, it connects to the peers in the network and begins downloading the file in small pieces. These small pieces, also known as "chunks" or "blocks," are downloaded simultaneously from multiple sources to expedite the download process.
Furthermore, torrent clients play a crucial role in managing the overall download and upload process. They handle the communication between peers, calculate download and upload speeds, and provide a user-friendly interface for monitoring and managing the torrents in progress.
By leveraging the rich metadata contained within torrent files, coupled with their ability to manage the download/upload process and connect users to the peer-to-peer network, torrent clients enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of torrenting. They enable users to easily access and share a vast range of files, including large multimedia files, software, and other types of digital content.
Pros and Cons of Torrent Clients
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Provides faster download speeds by leveraging multiple sources | Potential exposure to copyrighted or malicious files |
| Efficient use of bandwidth through sharing among peers | Requires reliable internet connectivity for optimal performance |
| Enables the distribution of large files without significant strain on servers | May be challenging for beginners due to technical nature |
| Facilitates decentralized sharing of files | Legal and ethical concerns related to copyright infringement |
Seeders, Leechers, and Swarms
In the world of torrenting, users can be classified into two categories: seeders and leechers. Seeders are individuals who have already downloaded the complete file and are actively sharing it with others in the network. They play a crucial role in the torrenting ecosystem, as they contribute to the availability and speed of file downloads.
On the other hand, leechers are users who are currently in the process of downloading the file. They rely on seeders to obtain the necessary data fragments to complete the download. Once a leecher has downloaded the entire file, they can become a seeder and contribute to the network by sharing the file with other leechers.
The number of seeders in a torrent greatly impacts the download speed and reliability. The more seeders a torrent has, the faster the download speed becomes. This is because a larger pool of seeders allows for a higher availability of file pieces to be shared among users, increasing the overall download rate.
Similarly, a higher number of seeders enhances the reliability of a torrent. If a seeder goes offline, there are still other seeders in the swarm that can provide the missing file pieces. This redundancy ensures that users can continue downloading a file even if some of the seeders are temporarily unavailable.
A swarm refers to the entire network of peers and seeders sharing a particular file. It represents the collective efforts of all participants in the torrenting process. When numerous seeders and leechers come together in a swarm, it creates a robust and efficient distribution system for large files.
"Seeders, leechers, and swarms are the building blocks of torrenting. They enable the distribution and sharing of files among users, ensuring faster downloads and increased reliability. By participating in a swarm, users contribute to the collective effort of providing access to valuable content for others."
Swarms in Action: Example Torrent
| File | Seeders | Leechers |
|---|---|---|
| Movie A | 356 | 721 |
| Software B | 153 | 289 |
| Game C | 432 | 568 |
Illustrated in the table above is an example of three torrents in action. Each torrent consists of a specific file, along with the number of seeders and leechers currently involved in the swarm. In this scenario, "Movie A" has 356 seeders and 721 leechers, "Software B" has 153 seeders and 289 leechers, and "Game C" has 432 seeders and 568 leechers.
The table highlights the varying sizes of the swarms formed around different files. Users can assess the popularity and health of a torrent by considering the number of seeders and leechers. A higher seeder count usually indicates a more established and stable network, leading to a faster and more reliable download experience.
Understanding seeders, leechers, and swarms is essential for torrenting enthusiasts to make informed decisions when choosing files to download. By joining a swarm with a significant number of seeders, users can maximize their chances of obtaining the desired file efficiently and quickly.
Torrent Indexers and Trackers
When it comes to finding and downloading torrent files, two key components play a vital role in making the process seamless: torrent indexers and trackers. Let's explore how these elements contribute to the efficient functioning of the torrent ecosystem.
Torrent Indexers:
Torrent indexers are websites that serve as repositories for a vast collection of torrent files. These platforms provide users with a searchable interface, enabling them to find the files they want to download easily. Torrent indexers aggregate metadata associated with each torrent file, including file size, file type, and the number of seeders and leechers.
This comprehensive database of torrent files simplifies the search process and allows users to evaluate different options before deciding on the file to download. Popular torrent indexers include The Pirate Bay, RARBG, and 1337x.
Trackers:
While torrent indexers store and organize files, trackers play a different role in the torrenting process. Trackers are servers that keep track of the peers participating in the torrent network. They act as intermediaries, facilitating the exchange of data between peers.
The primary function of trackers is to maintain a list of available peers and their IP addresses, allowing torrent clients to connect to each other. Although trackers don't directly handle the transfer of data, they serve as a crucial index or search engine for individuals in search of torrents.
Unlike torrent indexers that host the files themselves, trackers focus on managing the peer-to-peer network and establishing connections between users. Popular trackers include OpenBitTorrent and PublicBT.
Comparison of Torrent Indexers and Trackers
| Aspect | Torrent Indexers | Trackers |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Host and organize torrent files | Maintain peer-to-peer network and facilitate connections |
| Role | Act as a repository of torrents | Keep track of peers and their IP addresses |
| Responsibility | Store and provide metadata about files | Coordinate data exchange between peers |
| Examples | The Pirate Bay, RARBG, 1337x | OpenBitTorrent, PublicBT |
Both torrent indexers and trackers contribute to the overall functioning and accessibility of the torrent ecosystem. While indexers store and provide access to the files, trackers facilitate the connections between individual users, creating a robust peer-to-peer network.
Now that we have a clearer understanding of how torrent indexers and trackers work, let's delve deeper into a different aspect of torrent technology in the next section.
Magnet Links
Magnet links provide an alternative and convenient method to initiate torrent downloads. Unlike traditional downloading where users need to obtain a separate torrent file, magnet links contain all the necessary information to connect directly to the network and start downloading the file. This streamlined process eliminates the need for manual file downloads and simplifies the overall experience for users.
When users click on a magnet link, their torrent client automatically identifies and connects to the corresponding peers in the network. It retrieves the necessary information, such as the file name, size, and file structure, to initiate the download process. Magnet links enable users to conveniently share and access files without the hassle of downloading and managing separate torrent files.
The use of magnet links offers several advantages. Firstly, it reduces the reliance on torrent indexers and trackers, as the necessary information is embedded within the magnet link itself. This decentralized approach enhances user privacy and facilitates direct connections between peers, resulting in faster and more efficient downloads.
"Magnet links simplify the torrenting process by providing a one-click solution for initiating downloads."
Magnet links have become increasingly popular in the torrenting community due to their ease of use and enhanced efficiency. They have become a standard feature in many popular torrent clients, allowing users to seamlessly access and download files directly from magnet links. This technology has transformed the way users interact with torrents, making the download process more accessible and user-friendly.
Comparison of Traditional Torrent Files and Magnet Links
| Traditional Torrent Files | Magnet Links |
|---|---|
| Require a separate torrent file to initiate downloads | Contain all the necessary information within the link itself |
| Reliant on torrent indexers and trackers for metadata | Decentralized approach, eliminating the need for external dependencies |
| Manual process of downloading and managing torrent files | One-click solution, simplifying the torrenting experience |
| Potential for torrent files to become outdated or unavailable | Magnet links are less prone to expiration or unavailability |
Benefits of Torrents
Torrents offer several advantages over traditional file downloading methods. One of the key benefits is the efficient distribution of files. When downloading a file using torrents, it is broken down into smaller pieces called chunks. Rather than downloading the entire file from a single source, torrents enable the simultaneous downloading of these chunks from multiple users. This allows for faster overall download speeds, as the workload is distributed among multiple sources.
In addition to efficient distribution, torrents are also bandwidth-efficient. With traditional downloading methods, a single server bears the brunt of all download requests. This can result in slow download speeds, especially when dealing with large files or high demand. Torrents, on the other hand, leverage a peer-to-peer sharing network, where users share the load of distributing the file. This reduces the strain on individual servers and ensures a more balanced distribution of bandwidth.
Comparing Traditional Downloading and Torrent Downloads
| Traditional Downloading | Torrent Downloads |
|---|---|
| Files downloaded from a single source | Files downloaded from multiple sources simultaneously |
| Relies on the bandwidth and processing power of a single server | Shared bandwidth and distribution of workload among peers |
| Slow downloads for large files or high demand | Faster downloads due to parallel downloading |
As shown in the table above, the use of torrents significantly improves download speeds and ensures an efficient distribution of large files. By leveraging the power of a peer-to-peer network, torrents offer a more reliable and speedy experience for users.
Legal and Ethical Concerns
Torrents have revolutionized content sharing and distribution, providing a powerful tool for users to connect and transfer large files. However, with this convenience comes a host of legal and ethical concerns that cannot be ignored.
One of the major issues surrounding torrents is copyright infringement. Some users exploit torrents to share copyrighted materials without proper authorization, violating the rights of content creators and raising significant legal and ethical concerns. Unauthorized sharing of copyrighted movies, music, software, and other digital content through torrents is not only illegal but also undermines the creative and financial efforts of those who produce such content.
It is important for users to understand that torrenting copyrighted materials without permission is a violation of intellectual property laws. Content creators and rights holders invest time, resources, and creativity into producing original works, and they rely on fair compensation for their efforts. Unauthorized distribution through torrents undermines this ecosystem, depriving creators of the recognition and financial reward they deserve.
To ensure a responsible and legal torrenting experience, it is crucial for users to respect copyright laws and only share content they have the right to distribute. This means obtaining permission from the copyright holder or utilizing legal sources when sharing files through torrents.
"Respecting copyright laws is not just a legal requirement; it is a fundamental ethical principle that acknowledges the value of creators' work and their right to control its distribution."
Additionally, it is essential to be aware of and adhere to the ethical considerations surrounding torrenting. As a user, it is important to exercise responsible behavior, both in terms of the content being shared and the impact of torrenting practices on the broader digital community.
While torrents can be a powerful tool for sharing legitimate content and open access resources, they can also serve as a breeding ground for piracy and the circulation of malicious files. Users should exercise caution when downloading files from unknown sources, as they could potentially contain malware, viruses, or other harmful content.
By exercising responsible torrenting practices, such as utilizing trusted sources, supporting legal distribution channels, and verifying the authenticity of files, users can help create a safer and more ethical torrenting environment. This not only protects content creators' rights but also contributes to the overall health and sustainability of the digital ecosystem.
Ultimately, striking a balance between free sharing and respecting copyright laws is crucial for a responsible and legal torrenting experience. By understanding the legal and ethical concerns associated with torrenting, users can make informed decisions and contribute to a more equitable digital space.
Staying Safe While Torrenting
Torrenting can be a convenient and efficient way to download and share files. However, it's crucial to prioritize safety and protect yourself from potential threats. By following a few simple guidelines and utilizing the right tools, you can enhance your security while torrenting.
Using Trusted Sources for Torrent Downloads
When downloading torrents, it's essential to use trusted sources. Avoid downloading from suspicious websites that may host malicious content or fake files. These sources can potentially expose your computer to viruses, malware, or other security risks. Stick to reputable torrent indexing sites or verified sources recommended by the torrenting community.
Utilizing Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
A virtual private network (VPN) is a valuable tool for safeguarding your online activities, including torrenting. VPNs encrypt your internet connection, making it virtually impossible for anyone to intercept or monitor your online activities. They create a secure and private tunnel between your device and the internet, preventing prying eyes, including your internet service provider (ISP), from tracking your online activities.
When using a VPN while torrenting, all your internet traffic is routed through the VPN server, hiding your IP address and providing anonymity. This added layer of security ensures that your identity remains protected, making it difficult for potential copyright enforcers or other parties to trace your torrenting activities back to you.
By using a VPN, you can torrent with peace of mind, knowing that your online activities are secure and private. However, it's important to choose a reputable and reliable VPN provider. Look for VPNs with a strict no-log policy, robust encryption protocols, and a wide network of servers to ensure optimal performance and privacy.
"The use of trusted sources for downloading torrents and the utilization of virtual private networks (VPNs) are essential for staying safe while torrenting."
Staying safe while torrenting is crucial to protect yourself from potential risks. By utilizing trusted sources for downloading torrents and using a reliable VPN, you can enjoy a safer and more secure torrenting experience.
The Future of Torrenting
As technology continues to advance, the torrenting landscape is expected to undergo significant changes. Evolving technologies have the potential to enhance the efficiency and security of torrenting, providing users with even better experiences.
New protocols and methods will likely emerge, introducing innovative ways of sharing and distributing files. These advancements may include improvements in file integrity verification, faster download speeds, and enhanced privacy features. As a result, users can expect more reliable and streamlined torrenting experiences in the future.
However, while evolving technologies offer exciting possibilities, the legal landscape surrounding torrenting remains complex and varies by jurisdiction. Some countries have implemented strict measures to combat copyright infringement through torrents, making it essential for torrenting communities to adapt and comply with changing regulations.
Conversely, other jurisdictions have adopted a more lenient approach, recognizing the benefits of peer-to-peer file sharing. These regions may prioritize educational initiatives and promote legal alternatives to piracy, fostering a more balanced approach to copyright protection.
Torrenting communities and industry stakeholders must navigate this nuanced legal landscape, working collaboratively to find ways to coexist with content creators' rights. Open communication and proactive engagement between all parties involved can help shape the future of torrenting, ensuring a responsible and sustainable ecosystem for sharing digital content.
The Role of Education and Collaboration
Education plays a crucial role in the future of torrenting. By increasing awareness of the legal implications surrounding copyright infringement and promoting responsible torrenting practices, users can contribute to a more ethical and lawful torrenting culture.
Collaboration between torrenting platforms, content creators, and copyright holders is also key. By fostering dialogue and seeking mutually beneficial solutions, these stakeholders can work together to address concerns and find common ground.
Ultimately, the future of torrenting relies on the continued evolution of technologies, a proactive approach to legal compliance, and a shared commitment to respecting intellectual property rights. Through ongoing innovation and responsible practices, torrenting can continue to thrive while upholding legal and ethical standards.
| Prospects | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Enhanced download speeds and file integrity | Varied legal landscape |
| Improved privacy features through encryption | Need for user education on copyright |
| Increased collaboration between stakeholders | Ensuring a responsible torrenting ecosystem |
In the future, torrenting is poised to benefit from evolving technologies, offering improved efficiency and security. However, the legal landscape presents a challenge, requiring torrenting communities to adapt to changing regulations. By fostering education and collaboration, the future of torrenting can promote responsible practices and coexist with content creators' rights.
Conclusion
Torrents have transformed the way we share and distribute large files, providing an efficient and decentralized solution. Through their unique peer-to-peer architecture and file division, torrents enable faster downloads and a more balanced distribution of bandwidth. They have revolutionized the digital landscape, empowering users with the ability to exchange files directly with one another.
However, it is crucial for users to exercise caution while engaging in file sharing. Adhering to legal and ethical standards is paramount to ensuring a responsible and safe torrenting experience. Users must respect copyright laws and only share content they have the right to distribute. By doing so, we can foster a sustainable environment for digital content sharing.
The future of torrenting presents both challenges and opportunities. As technology continues to advance, we can expect evolving protocols and methods that enhance the efficiency and security of torrenting. However, it is important to navigate the changing legal landscape. Different jurisdictions have different perspectives on torrenting, necessitating adaptation and coexistence with content creators' rights.
Ultimately, file sharing through torrents has reshaped the way we distribute and access digital content. As we move forward, let us embrace the potential of torrents while maintaining a responsible and ethical approach to ensure the longevity and positive impact of this revolutionary technology.
FAQ
How do torrents work?
Torrents work by utilizing the BitTorrent protocol, which operates over a peer-to-peer (P2P) network. This allows users to directly share and receive files from one another, making the process more efficient. Torrents break large files into smaller pieces, which are downloaded simultaneously from multiple sources, resulting in faster downloads and more efficient file transfers.
What are torrent clients?
Torrent clients are software applications that facilitate torrent downloading and sharing. They interpret torrent files, which contain metadata about the files being shared and information about the network. Torrent clients play a crucial role in managing the download/upload process and connecting users to the peer-to-peer network.
What are seeders, leechers, and swarms?
Seeders are individuals who have already downloaded the complete file and are sharing it with others. Leechers are users who are currently downloading the file. A swarm refers to the entire network of peers and seeders sharing a certain file. The more seeders a torrent has, the faster the download speed and increased reliability.
What are torrent indexers and trackers?
Torrent indexers are websites that host torrent files, allowing users to search and find the files they want to download. These websites act as a repository of torrent files and provide a searchable interface for users. Trackers, on the other hand, are servers that keep track of the peers in the network and facilitate the exchange of data between them. While trackers are often not directly involved in the transfer of data, they serve as an index or search engine for people looking for torrents.
What are magnet links?
Magnet links are an alternative way to initiate torrent downloads. Instead of downloading a torrent file, users can click on a magnet link, which contains all the necessary information for the torrent client to connect to the network and start downloading the file. Magnet links eliminate the need for downloading a separate torrent file and make the process more streamlined.
What are the benefits of using torrents?
Torrents offer several advantages over traditional file downloading methods. The files are broken into smaller pieces, allowing for faster overall download speeds. Additionally, torrents are bandwidth-efficient as users share the load of distributing the file, reducing the strain on individual servers. This decentralized approach also provides a more balanced distribution of bandwidth and ensures efficient distribution of large files.
What are the legal and ethical concerns of torrenting?
While torrents are a powerful tool for sharing and distributing content, they are also associated with copyright infringement. Sharing copyrighted materials without proper authorization raises legal and ethical concerns. It is essential for users to respect copyright laws and only share content they have the right to distribute to ensure a responsible and legal torrenting experience.
How can I stay safe while torrenting?
To ensure a safe torrenting experience, it is important to use trusted sources for downloading torrents and to avoid downloading from suspicious websites that may host malicious content or fake files. It is also highly recommended to use a virtual private network (VPN) while torrenting. VPNs encrypt your internet connection, providing anonymity and privacy, and protect your identity from prying eyes.
What does the future hold for torrenting?
As technology continues to advance, the torrenting landscape is likely to evolve as well. New protocols and methods may enhance the efficiency and security of torrenting, offering users even better experiences. However, the legal perspective on torrenting varies by jurisdiction, and torrenting communities need to adapt to changing legal landscapes and find ways to coexist with content creators' rights.
What is the conclusion about torrenting?
Torrents have reshaped the digital landscape, providing an efficient and decentralized way of sharing large files. Their unique peer-to-peer architecture and division of files into smaller pieces enable faster downloads and a more balanced distribution of bandwidth. While torrents offer numerous benefits, users must exercise caution and adhere to legal and ethical standards to ensure a responsible and safe torrenting experience.